A custom Home Assistant integration that monitors cable modem signal quality, power levels, and error rates. Perfect for tracking your internet connection health and identifying potential issues before they cause problems.
Monitor your cable modem's signal quality, errors, and connection health in real-time
⭐ If you find this integration useful, please star this repo! It helps others discover the project and shows that the integration is actively used.
🤖 AI-Assisted Development: This project uses AI-assisted development (Claude) to accelerate implementation while maintaining human oversight for architecture and community decisions.
- Installation Guide
- Supported Modems
- Troubleshooting Guide
- Contributing Guide
- Development (for contributors)
📖 See the Getting Started Guide for development environment setup.
Quick start:
git clone https://github.com/solentlabs/cable_modem_monitor.git
cd cable_modem_monitor
./scripts/setup.sh # Local Python setup
# OR open in VS Code and click "Reopen in Container" for Dev ContainerWhat it monitors:
- 📊 Signal Quality: Power levels, SNR, frequency for every channel
⚠️ Error Tracking: Corrected & uncorrected errors per channel- 🔌 Connection Health: Status, uptime, and last boot time
- 💓 Modem Health: Real-time ping and HTTP latency monitoring
- 📈 Trends: Full historical data for analysis and graphing
What it does:
- 🔄 Remote Control: Restart your modem from Home Assistant
- 🤖 Automation Ready: Trigger actions on signal degradation or errors
- 🔐 Privacy First: All local processing, automatic PII sanitization
- 🛡️ Security Focused: CodeQL scanned with 6 custom security queries
- 🔌 Plug & Play: Easy UI configuration, no YAML editing needed
Track your cable modem's health with comprehensive dashboards and real-time monitoring:
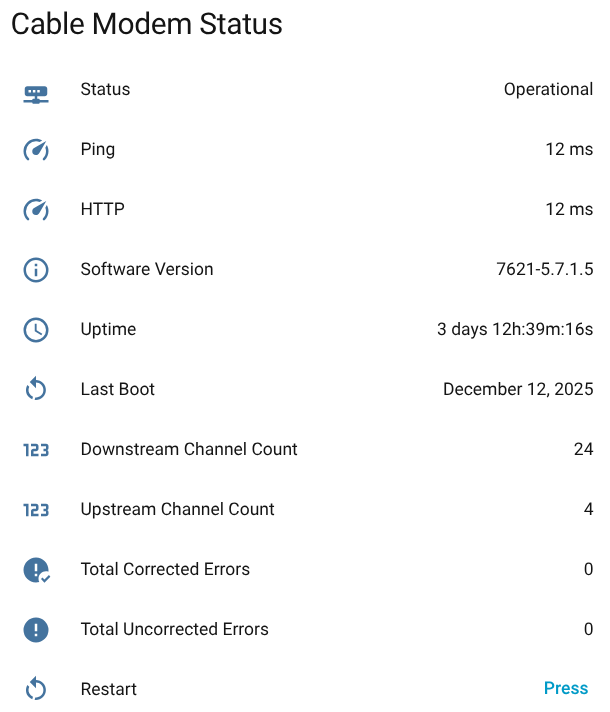
Complete dashboard showing connection status, signal quality, and error tracking
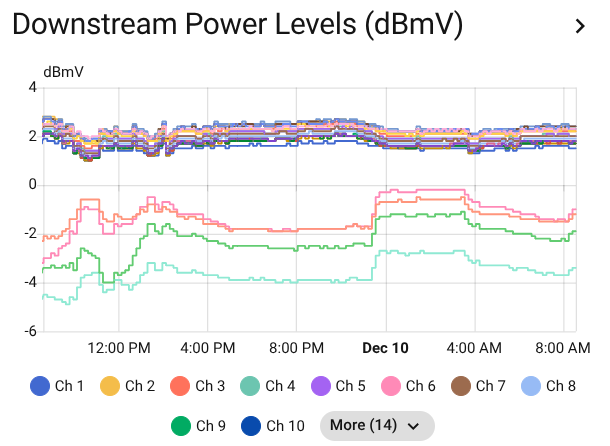
Real-time power level monitoring across all downstream channels
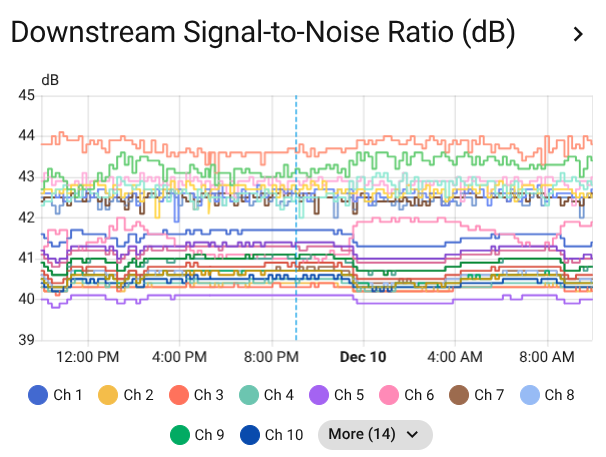
SNR tracking helps identify signal quality issues before they cause problems
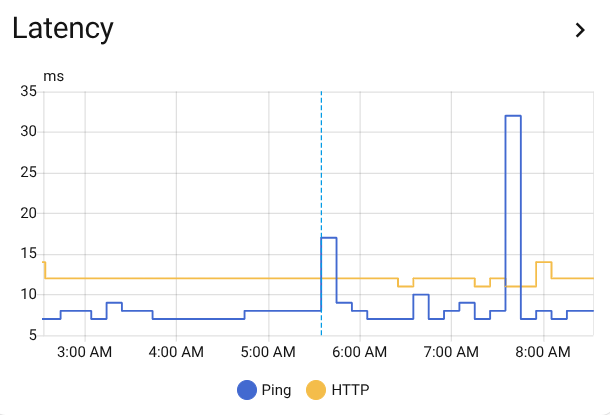
Ping and HTTP latency monitoring for real-time health assessment
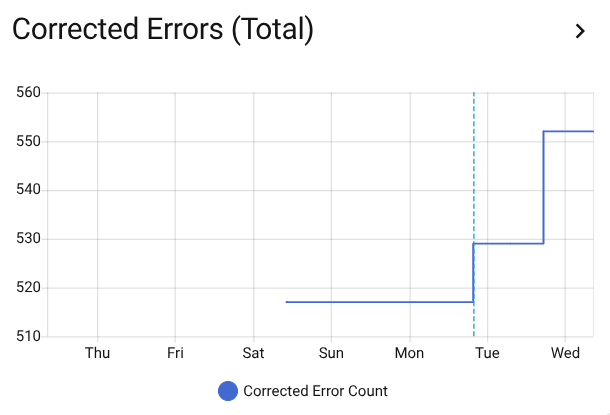
Track corrected errors over time to spot developing line issues
- Easy Setup: Configure via Home Assistant UI - no YAML editing required
- Comprehensive Channel Monitoring: Tracks all downstream and upstream channels
- Per-Channel Metrics:
- Power levels (dBmV)
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR in dB)
- Frequency (Hz)
- Corrected/Uncorrected errors
- Summary Sensors: Total corrected and uncorrected errors across all channels
- Unified Status: Single sensor showing operational state (Operational/Degraded/Not Locked/Unresponsive)
- System Information: Software version, uptime, channel counts, and last boot time
- Health Monitoring: Real-time modem health checks with:
- Ping latency monitoring
- HTTP response time tracking
- Automatic health status assessment
- Circuit breaker pattern for reliability
- Modem Control: Restart your modem directly from Home Assistant
- Automation-Friendly: Last boot time sensor with timestamp device class for reboot detection
- Consistent Entity Naming: All entities use
cable_modem_prefix for predictability - Historical Data: All metrics are stored for trend analysis
- Dashboard Ready: Create graphs and alerts based on signal quality
- Extensible: Plugin architecture makes adding new modem models easy
- Well Tested: 440+ test cases with comprehensive coverage
- Type Safe: Full type hints and mypy validation
This integration supports modems from ARRIS, Motorola, Netgear, and Technicolor. Compatibility varies based on firmware versions and ISP customizations.
📊 View the Modem Fixture Library - Complete list with DOCSIS versions, ISP compatibility, verification status, and model timelines.
If your modem isn't listed, you can still install the integration! It will enter Fallback Mode which:
- Allows installation to succeed
- Enables the "Capture HTML" diagnostics button
- Lets you provide HTML samples to help add support for your modem
- See How to Help Add Support below
Using a modem marked with asterisk (*)? Report it working to help other users!
If your modem isn't supported or you'd like to help expand compatibility, we'd love your help!
📖 See the Modem Request Guide for step-by-step instructions on capturing and submitting diagnostic data.
Want to develop the parser yourself? See the Contributing Guide for details.
Prerequisites: You must have HACS installed. If you don't have HACS yet:
- Go to Settings → Add-ons → Add-on Store
- Click three dots (⋮) → Repositories
- Add:
https://github.com/hacs/addons - Install and start the "Get HACS" add-on
- Restart Home Assistant
- Go to Settings → Devices & Services → Add Integration → Search for "HACS"
- Complete HACS setup (requires free GitHub account)
Installing Cable Modem Monitor via HACS:
- Open HACS from the Home Assistant sidebar
- Search for "Cable Modem Monitor"
- Click "Download"
- Restart Home Assistant
- Add the integration: Settings → Devices & Services → Add Integration → Cable Modem Monitor
- Download the latest release
- Extract the zip file
- Copy the
custom_components/cable_modem_monitorfolder to your Home Assistant'sconfig/custom_components/directory - Restart Home Assistant
- Go to Settings → Devices & Services
- Click "+ Add Integration"
- Search for "Cable Modem Monitor"
- Enter your modem's IP address (typically
192.168.100.1)
Already have Cable Modem Monitor installed via HACS? You can switch to any branch, tag, or commit to test new features before they're officially released:
- Go to Developer Tools → Actions
- Search for
update.install - Under Targets, select your Cable Modem Monitor update entity (e.g.,
update.cable_modem_monitor_update) - In the version field, enter the branch name (e.g.,
feat/new-modem-parser) - Click Perform action
- Restart Home Assistant
The version field accepts branch names, tags, full commit SHAs, or the first 7 characters of a commit SHA.
💡 Thanks to @ChBi89 for documenting this workflow!
- Find your modem's IP address: Usually
192.168.100.1or192.168.0.1 - Verify web interface access: Open
http://192.168.100.1(or your modem's IP) in a browser - Add the integration:
- Settings → Devices & Services → Add Integration
- Search for "Cable Modem Monitor"
- Enter the IP address
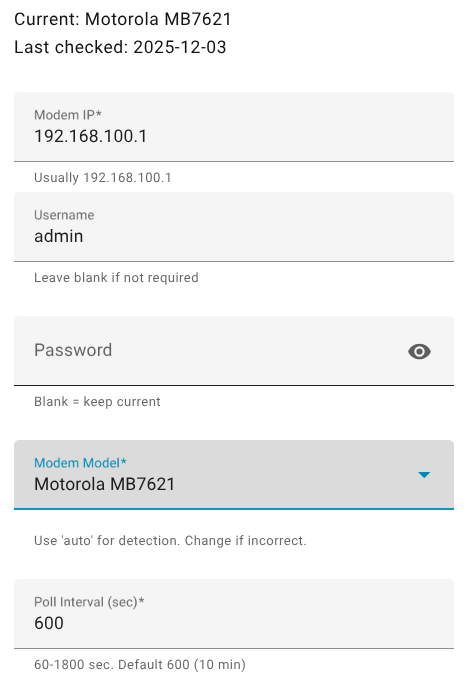
After installation, you can configure additional settings:
- Go to Settings → Devices & Services
- Find Cable Modem Monitor and click Configure
- Available options:
- Modem IP Address: Update if your modem's IP changes
- Username/Password: Update authentication credentials
- Modem Model: Select your modem model or use "auto" for automatic detection (recommended)
- Polling Interval: How often to check modem status (60-1800 seconds, default: 600 - 10 minutes)
- History Retention: Number of days to keep when using Clear History button (1-365 days, default: 30)
Configuration options available through the Settings UI
All sensors use the cable_modem_ prefix for consistent entity naming and easy identification.
Entity Naming Pattern:
- System sensors:
sensor.cable_modem_{metric}(e.g.,sensor.cable_modem_status) - Channel sensors:
sensor.cable_modem_{direction}_ch_{number}_{metric}- Example:
sensor.cable_modem_ds_ch_1_power(downstream channel 1 power) - Example:
sensor.cable_modem_us_ch_3_frequency(upstream channel 3 frequency)
- Example:
sensor.cable_modem_status: Unified pass/fail status combining connection, health, and DOCSIS lock state- Operational: All good - data parsed, DOCSIS locked, reachable
- ICMP Blocked: HTTP works but ping fails (check parser
supports_icmpsetting) - Partial Lock: Some downstream channels not locked
- Not Locked: DOCSIS not locked to ISP
- Parser Error: Modem reachable but data couldn't be parsed
- Unresponsive: Can't reach modem via HTTP
sensor.cable_modem_software_version: Modem firmware/software versionsensor.cable_modem_system_uptime: How long the modem has been runningsensor.cable_modem_last_boot_time: When the modem last rebooted (timestamp device class)sensor.cable_modem_ds_channel_count: Number of active downstream channelssensor.cable_modem_us_channel_count: Number of active upstream channels
sensor.cable_modem_ping_latency: Ping response time in millisecondssensor.cable_modem_http_latency: HTTP response time in milliseconds
sensor.cable_modem_total_corrected_errors: Total corrected errors across all downstream channelssensor.cable_modem_total_uncorrected_errors: Total uncorrected errors across all downstream channels
Replace X with the channel number (1-32 depending on your modem):
sensor.cable_modem_downstream_ch_X_power: Power level in dBmVsensor.cable_modem_downstream_ch_X_snr: Signal-to-Noise Ratio in dBsensor.cable_modem_downstream_ch_X_frequency: Channel frequency in Hzsensor.cable_modem_downstream_ch_X_corrected: Corrected errorssensor.cable_modem_downstream_ch_X_uncorrected: Uncorrected errors
Replace X with the channel number (1-8 depending on your modem):
sensor.cable_modem_upstream_ch_X_power: Transmit power level in dBmVsensor.cable_modem_upstream_ch_X_frequency: Channel frequency in Hz
button.cable_modem_restart_modem: Restart your cable modem remotely
cable_modem_monitor.clear_history: Clear old historical data (keeps specified number of days)cable_modem_monitor.cleanup_entities: Remove orphaned entities from registry (useful after upgrades)
- Ideal range: -7 to +7 dBmV
- Acceptable: -15 to +15 dBmV
- Poor: Below -15 or above +15 dBmV
- Excellent: Above 40 dB
- Good: 33-40 dB
- Acceptable: 25-33 dB
- Poor: Below 25 dB
- Ideal range: 35-50 dBmV
- Acceptable: 30-55 dBmV
- Poor: Below 30 or above 55 dBmV
- Corrected errors: Normal in small amounts; modem can fix these
- Uncorrected errors: Indicate data loss; any sustained increase is concerning
- Monitor trends: Sudden increases may indicate line issues
Ready-to-use dashboard and automation examples are available in the Examples Guide.
Includes:
- Complete dashboard YAML for monitoring all channels
- Automations for error alerts, SNR warnings, and auto-restart
- Last boot time display format options
📖 See the Troubleshooting Guide for solutions to common issues including connection problems, missing sensors, and duplicate entities.
Contributions are welcome! If you have:
- Support for additional modem models
- Bug fixes
- Feature improvements
Please see the Contributing Guide for details on how to add support for your modem, run tests, and submit changes.
- 100% Local: All data stays on your Home Assistant instance - no cloud services
- Read-Only: Only reads data from your modem (never modifies configuration)
- PII Sanitization: Automatic removal of sensitive data from diagnostics
- IP addresses, MAC addresses, serial numbers automatically redacted
- Safe to share diagnostic files for support
- Secure Credentials: Stored in Home Assistant's encrypted storage
- CodeQL Scanning: Automated security analysis on every commit
- 100+ standard security queries (OWASP Top 10, CWE coverage)
- 6 custom security queries specific to cable modem integration:
- HTTP requests without timeouts
- Command injection prevention
- XML External Entity (XXE) protection
- Hardcoded credential detection
- SSL/TLS misconfiguration checks
- Path traversal prevention
- Security Documentation: See CodeQL Testing Guide for details
- Vulnerability Reporting: See SECURITY.md for responsible disclosure
- HTTP Basic Authentication
- Form-based authentication
- HNAP/SOAP authentication
- No authentication (for open modems)
MIT License - see LICENSE file for details
- Changelog - Version history and release notes
- Contributing Guide - How to contribute code or add modem support
- Troubleshooting Guide - Common issues and solutions
- Examples - Dashboard and automation YAML
- Modem Request Guide - Help add support for your modem
- AI Context - Project context for AI assistants
Created for monitoring Cox Cable Motorola modems, but designed to work with various cable modem brands.
Solent Labs™ is not affiliated with Arris, Motorola, Netgear, or any ISP. All product names are trademarks of their respective owners. Use this software at your own risk.