SLURP : Smart Land Use Reconstruction Pipeline
SLURP is your companion to compute a simple land-use/land-cover mask from Very High Resolution (VHR) optical images. It proposes different few or unsupervised learning algorithms that produce one-versus-all masks (water, vegetation, shadow, urban). Then a final algorithm stacks them all together and regularize them to obtain into a single multiclass mask.
SLURP uses some global data, such as Global Surface Water (Pekel) for water detection or World Settlement Footprint (WSF) for building detection.
Data preparation can be achieved with Orfeo ToolBox or other tools, in order to bring all necessary data in the same projection. You can either build your mask step by step, or use a batch script to launch and build the final mask automatically.
SLURP can be installed with pip :
pip install slurp-masks
Once your environment is ready, you can prepare data with slurp_prepare and then compute SLURP masks with slurp_watermask, slurp_urbanmask, etc.
Documentation is available on Read the docs
A tutorial is available : Tutorial.md.
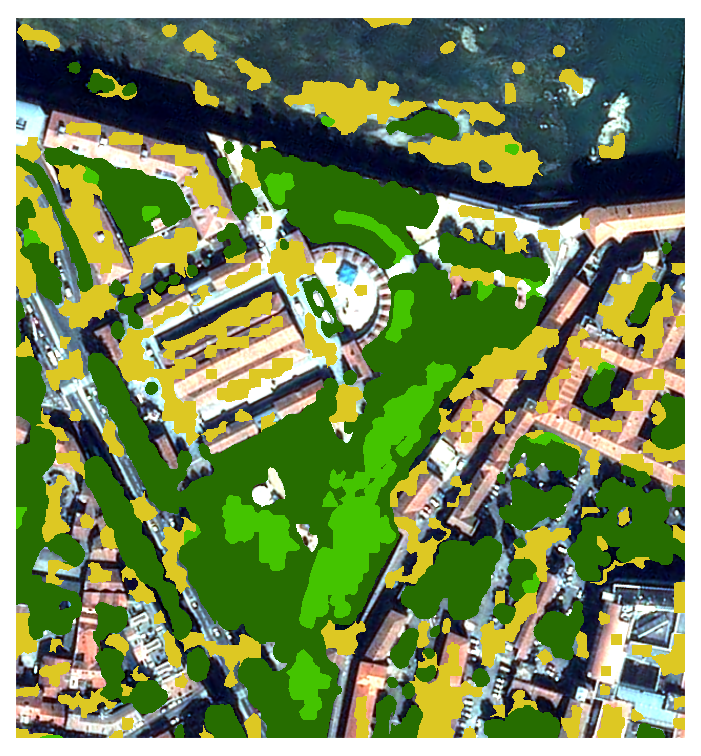
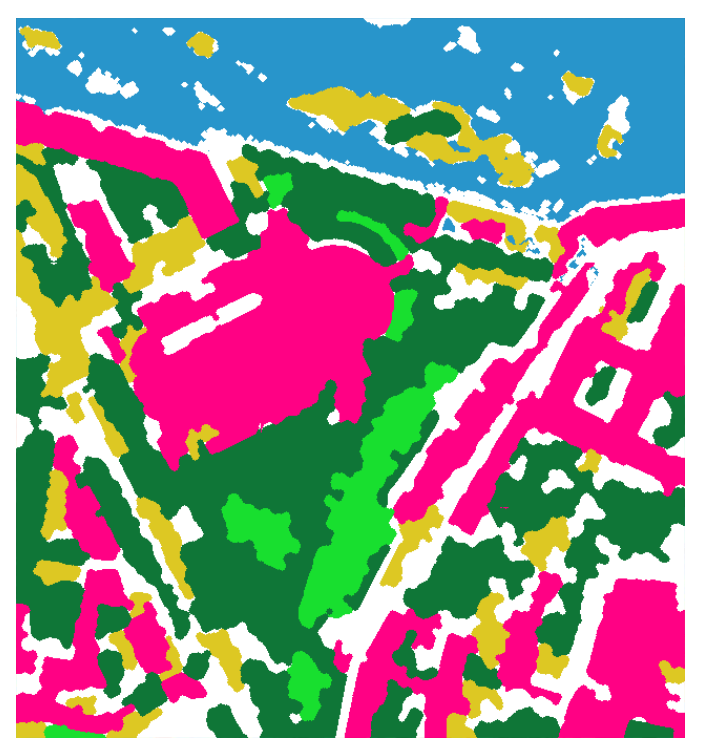
SLURP computes several single-class masks (one versus all) and then stacks (and regularize) them into a multi-class map.
SLURP needs to superimpose some external data so it fits your target VHR image. It can be done through OTB Superimpose application
mkdir out
# Superimpose Pekel, Hand and WSF with OTB
#
# /!\ Adapt path depending on where your global Pekel database (resp. HAND, WSF) is located
otbcli_Superimpose -inr <your VHR image.tif> -inm <path to Global Surface Water Pekel occurrence file> -out "out/pekel.tif?&gdal:co:TILED=YES&gdal:co:COMPRESS=DEFLATE" uint8 -interpolator nn
otbcli_Superimpose -inr <your VHR image.tif> -inm <path to Heigh Above Nearest Drainage map> -out "out/hand.tif?&gdal:co:TILED=YES&gdal:co:COMPRESS=DEFLATE"
otbcli_Superimpose -inr <your VHR image.tif> -inm <path to World Settlement Footprint map> -out "out/wsf.tif?&gdal:co:TILED=YES&gdal:co:COMPRESS=DEFLATE" uint8 -interpolator nn
# Prepare : computes primitives (NDVI / NDWI / textures)
slurp_prepare <your_slurp_conf.json> -file_vhr <your VHR image.tif>
# Watermask : learn from Pekel database and predict water occurrence
slurp_watermask out/effective_used_config.json
# Vegetationmask : segment image and apply clustering method to detect low/high vegetation
slurp_vegetationmask out/effective_used_config.json
# Shadowmask : threshold RGB and NIR to detect shadows
slurp_shadowmask out/effective_used_config.json
# Urbanmask : learn from WSF and compute urban probability
slurp_urbanmask out/effective_used_config.json
# Stack : regularize all the previous masks together
slurp_stackmasks out/effective_used_config.json
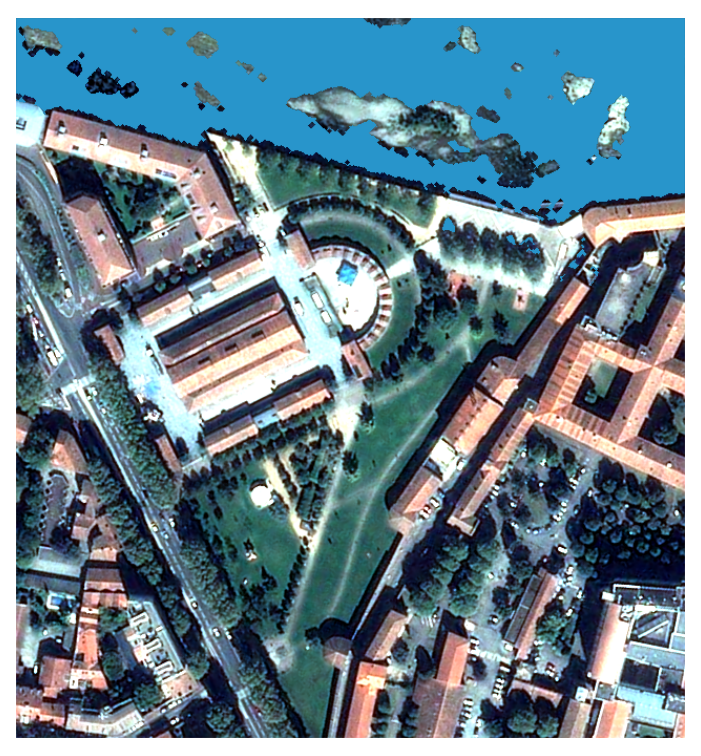
SLURP is designed to compute a simple land cover map (water, low/high vegetation, bare groud, buildings) from a VHR (Very High Resolution) image with 4 bands (Red, Green, Blue, Near-Infrared). SLURP is based on few or unsupervised algorithms (random forest, clustering, segmentation) that need some auxiliary data for training step.
It had been validated with Pleiades and tested with WordView, CO3D, Pleiades NEO images. It shall also work with images with lower resolution (ex : SPOT 6/7).
| Data | Step / usage | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Pekel (Global Surface Water) | Water mask prediction : Water occurrence [0-100] during the last 30 years, used to learn a water prediction model (MANDATORY) | The global map is mandatory but you can also use some data by month |
| Hand MERIT | Water mask prediction : Map of height above nearest drainage used to optimize choice of "non water" samples in the training step (OPTIONAL) | Free after registration (other kind of HAND maps exist) |
| WSF 2019 (World Settlement Footprint) | Urban mask prediction : global buildings map used to learn a building prediction model (MANDATORY) | Could be replaced by a better resolution map if available (ex : OSM buildings) |
| ESA WorldCover | Vegetation mask configuration Global land cover map (10m resolution) used to customize vegetation clustering (OPTIONAL) | Very helpful to parameterize balance between non-vegetation / low and high vegetation clusters (see vegetation mask algorithm) |
| Copernicus WBM | Stack mask : Water Body Mask from Copernicus, used to classify each water body from the watermasl (OPTIONAL) | If used, the final map will contain river, lake, sea classes |
Some masks need auxiliary files and some primitives computed from your VHR image.
These data must be on the same projection, resolution and bounding box as the VHR input image to enable mask computation.
You can generate this data yourself or use the prepare command (slurp_prepare) available in SLURP.
The prepare script enables :
- Computation of stack validity (with or without a cloud mask)
- Computation of NDVI and NDWI
- Extraction of largest Pekel file (in sensor mode only)
- Extraction of largest HAND file (in sensor mode only)
- Extraction of WSF file (in sensor mode only)
- Extraction of Water Body Mask (if needed, in sensor mode only)
- Computation of texture file (convolution on NIR band)
Water model is learned from Pekel (Global Surface Water) reference data and is based on NDVI/NDWI2 indices.
First the algorithm will pick-up water (and non-water) samples from your image, by using Pekel as a prior.
Then, a random forest learns how to predict water and predicts a raw mask on the whole image. The predicted mask is cleaned with Pekel, possibly with HAND (Height Above Nearest Drainage) maps and post-processed to clean artefacts.
It is possible to adapt a lot of parameters (see slurp_watermask -h) to adapt learning parameters, add other features (-layers <features in an other raster>), etc.
Vegetation mask are computed with an unsupervised clustering algorithm. First some primitives are computed from VHR image (NDVI, NDWI2, textures). Then a segmentation is processed (SLIC) and segments are dispatched in several clusters depending on their features. A final labellisation affects a class to each segment (ie : high NDVI and low texture denotes for low vegetation).
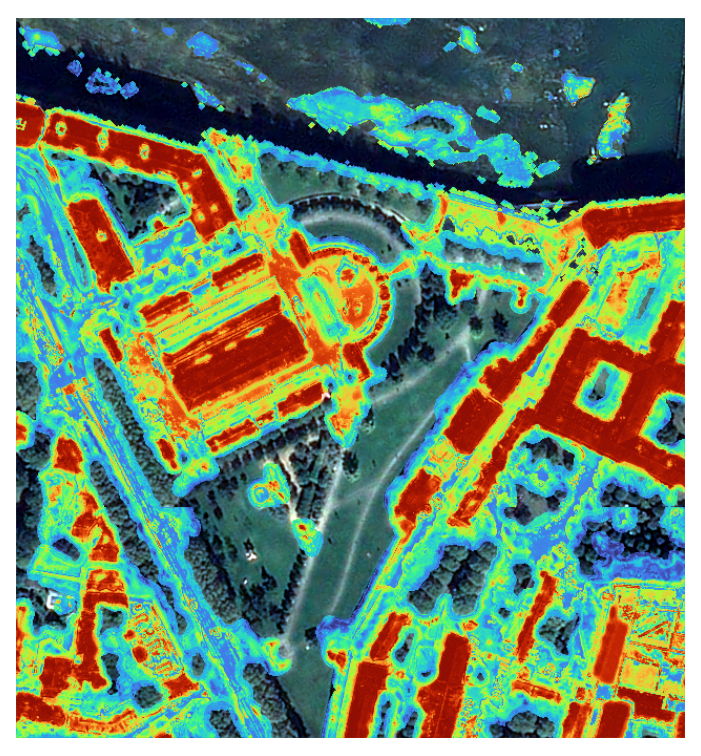
An urban model (building) is learned from WSF reference map. The algorithm can take into account water and vegetation masks in order to improve samples selection (non building pixels will be chosen outside WSF and outside water/vegetation masks). The output is a "building probability" layer ([0..100]) that is used by the stack algorithm.
Shadow mask detects dark areas (supposed shadows), based on two thresholds (RGB, NIR). A post-processing step removes small shadows, holes, etc. The resulting mask is a three-classes mask (no shadow, small shadow, big shadows). The big shadows are used in the stack algorithm in the regularization step.
The stack algorithm takes into account all previous masks to produce a 6 classes mask (water, low vegetation, high vegetation, building, bare soil, other) and an auxiliary height layer (low / high / unknown).
The algorithm regularizes urban mask with a watershed algorithm based on building probability and context of surrounding areas.
This algorithm first computes a gradient on the image and fills a marker layer with known classes. Then a watershed step helps to adjust contours along gradient image, thus regularizing buildings shapes.
The stack algorithm can also categorize water bodies (lake, river, sea) if you provide a general water body mask as an input.
You can override the JSON with CLI arguments. For example : slurp_stackmasks <JSON file> -file_vhr <VHR input image> -remove_small_objects 500 -binary_closing 3
SLURP vegetation algorithm had been described in the following paper : Smart Land Use Masks : A Simple and Robust Approach to Produce Low/High Vegetation Masks from a Single High Resolution Satellite Image
This package was created with PLUTO-cookiecutter project template.
Inspired by main cookiecutter template and CARS cookiecutter template